- Shipped today!
- Free shipping from € 45
- Postpay possibility
- Review score 9.4
- Earn reward points
- Shipped today!
- Free shipping from € 45
- Postpay possibility
- Review score 9.4
- Earn reward points
- Home
- Health Goals
- Muscles
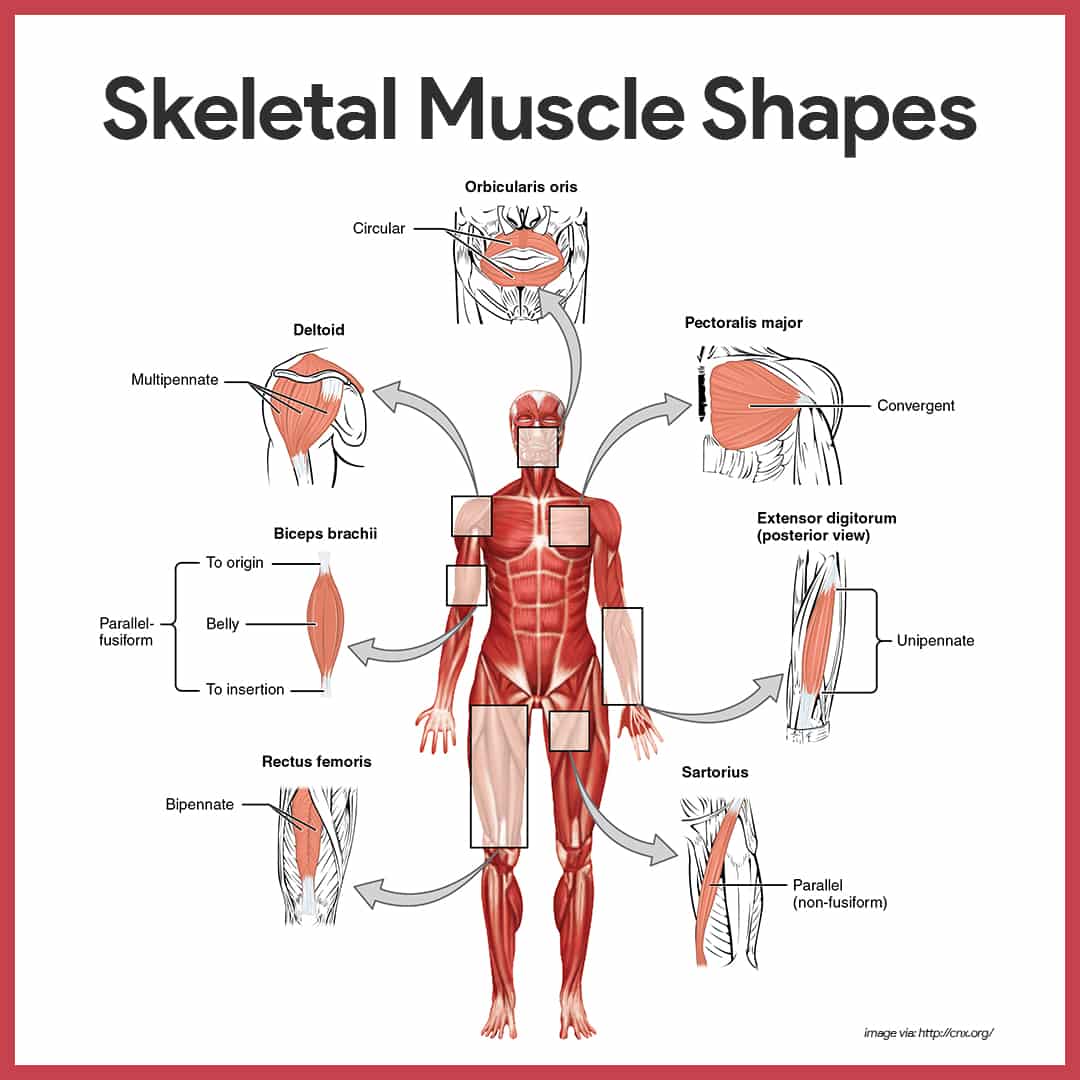
What are the muscles?
Muscles are tissues that contract and cause movement. There are three major types of muscle:
- Cardiac: your heart muscle, which is different from all other types of muscle in the body and contracts involuntary.
- Smooth: muscles that line our blood vessels, responsible for most of our involuntary processes (i.e. pushing food through the gastrointestinal tract, urination, blood circulation)
- Skeletal: a type of muscle that is attached to our skeleton, there are 640 skeletal muscles. We can see, feel and flex these muscles.
Muscle is extremely complex in molecular action (what happens when you look at a muscle under a microscope) yet simple in function. All muscles really do is contract (become shorter) and relax (back to resting length), obviously, this is an oversimplification. However, for this brief overview, it serves its purpose.
One important distinction, although not the specific topic is the difference between ligaments and tendons, many people can get confused, so see this short definition below.
- Ligaments connect bones to other bones
- Tendons connect muscle to bone
(Source: Nurselabs)
Muscle-tendon combos stretch across all joints connecting your upper leg to the lower leg and lower arm to the upper arm. This facilitates movement (one bone can move in relation to the other bone).
What is the function of skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscle is what we are trying to maintain and build for the most part. Anytime you hit the weights you are trying to increase skeletal muscle. It has various functions, including, but not limited to:
- Maintains posture
- Oxygen consumption
- Energy metabolism
- Protect vital organs in the body
- Balance
- Energy storage
- Reduce injury risk
(Source: ScienceDirect)
How much muscle mass can I build?
How can I increase my muscle mass?
From a nutritionally perspective calories and protein are most important. First, to provide sufficient energy (calories) to build the new muscle tissue. Second, to provide the raw material (protein) for construction. Okay, well how much? this is where things become tricky. However, we can give general guidelines to follow and then based on your response to whatever training program and nutrition protocol you follow, you can adjust intake to achieve the desired response (Source: NCBI).
- Protein: Most people should consume 1.6-2.4g/kg of body mass (Source: NCBI)
- Calories: Thes best approach here is to redirect you to the NIH website (Source: NIH) bodyweight calculator. Here, you can input all your personal data and see how much calories (estimate) you need to lose, maintain or gain weight. This calculator has been validated and is a reliable tool (Source: NCBI).
As shown below, the general physical activity guidelines, state - "Adults should also do muscle-strengthening activities at moderate or greater intensity that involve all major muscle groups on 2 or more days a week, as these provide additional health benefits". Muscle provides many benefits outside of aesthetics, remember this as we all age and grow old eventually.
For physical activity, those with no underlying health conditions (confirm with your doctor) or complications, following general physical activity guidelines from the World Health Organisation are recommended (Source: BJSM):
"It is recommended that:
- All adults should undertake regular physical activity;
- Adults should do at least 150–300 min of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity, or at least 75–150min of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate-intensity and vigorous-intensity activity throughout the week for substantial health benefits;
- Adults should also do muscle-strengthening activities at moderate or greater intensity that involve all major muscle groups on 2 or more days a week, as these provide additional health benefits"
Other Lifestyle Factors
- Avoid any and all forms of smoking (decrease aerobic capacity)
- Avoid excessive alcohol intake (impair muscle growth)
- Ensure high quality and quantity sleep regularly (promote muscle growth and repair)
- Consume a healthy and well-balanced diet (Promote muscle repair and recovery)
- Minimise other stressors in personal and professional life (stress can decrease hormones beneficial for muscle growth and increase stress hormones which creates a suboptimal environment for growth)
(Source: NCBI)
General principles of a healthy, balanced diet rich in omega-3, vitamins and minerals, and fibre are associated with overall health and, therefore, a well functioning system that is efficient in producing new muscle tissue.
Consume plenty of fruit & vegetables. Supplementation may be beneficial to fill the gaps as discussed in "additional considerations" below.
Additional Considerations
While consumption of most nutrients through natural or fortified foods is preferred, some nutrients may occasionally need supplementation. Especially for restrictive diets or those that lack variety.
As a general rule try to consume 5-7 servings of fruit and vegetables a day. Importantly, if you do not consume animal products you should consult your healthcare professional to discuss and consider a vitamin B12 supplement. The main issue with vitamin B12 is everything is fine until it's not. Meaning its a silent threat to our health, we have stores in the liver that can last 1-2 years and even longer in some instances. Hence, get ahead and check your status, the first sign of vitamin B12 deficiency can, unfortunately, have already caused irreversible damage. Vitamin D is another at risk-nutrient and should be supplemented from October-March in countries of northern latitude (north of the equator, Ireland, UK, Denmark, etc.) (Source: NCBI, MDPI).
Supplements worth considering are
- Creatine: Help with training intensity, muscle repair and recovery.
- Caffeine: Useful training aid at high intensities, decrease perceived exertion
- Protein: Convenient, high quality and cheap
- Vitamin D: Read above, and involved in muscle repair
- Omega-3: Involved in muscle repair processes
Want to learn more?
Here at Plent, we are different from most other supplement retailers out there. We are committed to consumer education and empowerment, and transparency and quality assurance of all our own supplements. For this reason, we want all our customers to have a full and rounded understanding of the world of supplementation. If you would like to read more about your muscles and how to build them, check out the links below:
Video & Articles
- Muscles, Part 1 - Muscle Cells: Crash Course A&P #21
- Muscles, Part 2 - Organismal Level: Crash Course A&P #22
- Muscle Gain & Exercise
- Data-Based Muscle, Strength, and Fat-Loss Targets to Set Realistic Training Goals
- Greg Nuckols Answers: What’s the Best Way to Build Muscle?
- Examine.com: Optimal Protein Intake Guide
















